MCAT Physics Practice Questions
/Prepare for MCAT Physics questions with practice problems
(Note: This resource also appears in our MCAT Ultimate Guide.)
----
Introduction
MCAT Physics Practice Passage #1
MCAT Physics Practice Passage #2
MCAT Physics Practice Passage #3
MCAT Physics Practice Questions (Standalone)
----
Introduction
The MCAT will be the longest and most difficult test that the majority of premeds take on their way to medical school. Within this beast of an exam, the MCAT includes difficult topics like physics, organic chemistry, and general chemistry.
Physics makes up 25 percent of your chemistry/physics section, give or take 5 percent. So, your exam will likely have between 12 and 18 physics questions. To put this in perspective, however, the entire exam is 230 questions, so physics makes up only around 5 to 7 percent of your entire exam.
Physics is a vast topic, but we’ve shown that it only shows up on a small percentage of your exam. So, how can you achieve a great MCAT score and ace physics questions without spending a disproportionate amount of time studying MCAT physics? In other words, how are you supposed to learn MCAT physics without sacrificing your performance in other sections that will yield more points, like MCAT psychology and sociology?
Practice, practice, practice! By taking physics practice problems, you’ll learn how the test-writers like to ask questions, the high-yield material that is likely to show up on your exam, and what information you should spend your valuable time studying.
Use the following three passages and five standalone questions to test your ability to apply your physics knowledge to real, MCAT-style passages. You’ll notice that each explanation for the passage-based questions has suggestions for what you should review if you miss a question. Good luck!
----
MCAT Physics Practice Passage #1
Researchers are interested in studying a novel optical system to model the human eye. The experimental set-up includes a lens, object, and image. The object is placed at various positions relative to the lens in order to produce different images.
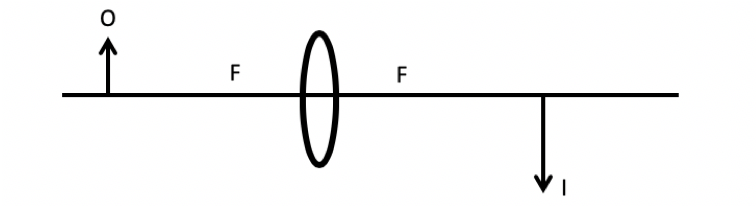
In Experiment 1, the experimental set-up appears as shown in Figure 1. The object is located at position O, the image is located at position I, and the focal length of the lens is shown at position F.
Figure 1. Experiment 1 set-up.
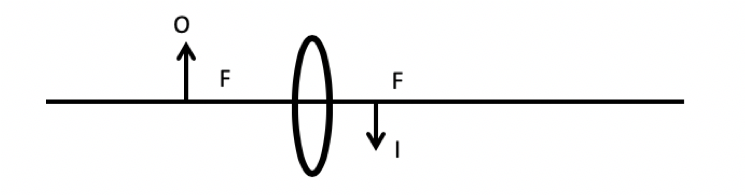
In Experiment 2, the researchers adjusted the position of the object resulting in a different location of the image. The experimental set-up appears as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Experiment 2 set-up.
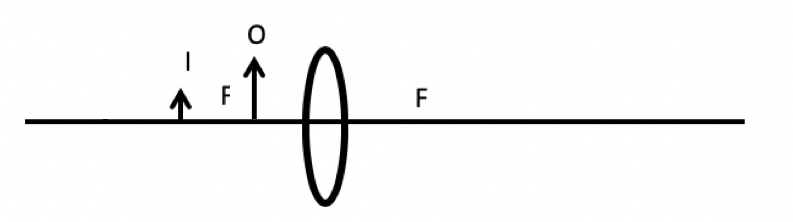
In Experiment 3, the researchers once again adjusted the position of the object. The experimental set-up appears as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Experiment 3 set-up.
Note: The information in this passage was created for the sole purpose of presenting an MCAT-style passage and should not be construed to be factually true.
1. Which of the following determines the focal length of the lens in Figure 1?
A) Radius of curvature of the lens
B) Image distance
C) Object distance
D) The level of lens magnification
2. In Experiment 1, suppose the object distance is 2 cm and the image distance is 3 cm. What is the focal length of the lens?
A) 1/2 cm
B) 3/4 cm
C) 6/5 cm
D) 7/9 cm
3. Which of the experiments produces a virtual image?
A) Experiment 1
B) Experiment 2
C) Experiment 3
D) None of the experiments produce a virtual image.
4. In Experiment 2, suppose the image distance is increased. What effect would this increase have on the absolute value for the magnification of the lens?
A) Increase
B) Decrease
C) Stays the same
D) No change
MCAT Physics Practice Passage #1 Answers and Explanations
1. The correct answer is A. The focal length of the lens is an intrinsic property of the lens that is based on the radius of curvature of the lens (choice A is correct; choices B, C, and D are incorrect).
Review optics.
2. The correct answer is C. The thin lens equation is given by:
$$ \frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{o} + \frac{1}{i}$$
Thus,
$$ \frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{3} = \frac{3}{6} + \frac{2}{6} = \frac{5}{6}$$
To obtain a value of f, we can take the reciprocal of this value. As a result, f must be equal to 6/5(choice C is correct; choices A, B, and D are incorrect).
Review thin lens equation.
3. The correct answer is C. In Experiment 3, the lens produces an object and image that are on the same side of the image, therefore producing a virtual image (choice C is correct; choices A, B, and D are incorrect).
Review optics.
4. The correct answer is A. The magnification formula is given by m = -i/o. Since the question asks for absolute value, the negative sign can be ignored. As i is increased, m also increases since the two variables are directly proportional (choice A is correct; choices B, C, and D are incorrect).
Review optics and the magnification equation.
Gain instant access to the most digestible and comprehensive MCAT content resources available. 60+ guides covering every content area. Subscribe today to lock in the current investments, which will be increasing in the future for new subscribers.